AI In Cybersecurity
Artificial Intelligence Driving the Future of Cybersecurity

Overview
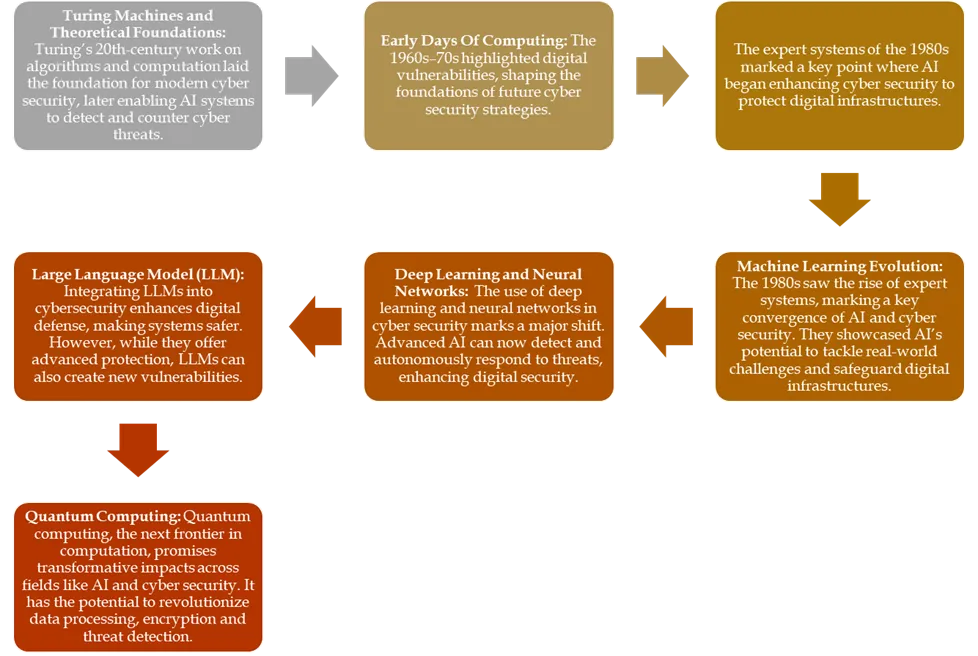
Cyber-attacks are increasing rapidly, costing businesses money and damaging their reputation. Security professionals deal with a lot of routine tasks, like fraud investigation and log analysis, which hinders their ability to handle changing threats. Artificial intelligence (AI) provides solutions that can help self-learn and adjust to new attack patterns, becoming increasingly necessary for dependable protection to keep up.

Implementing AI requires significant investment in development, infrastructure, personnel and integration. Its adoption is crucial, driving the growing cost and importance of AI in cybersecurity.
Evolution of AI in Cybersecurity
Key Factors Driving the Industry Growth
Behavioral Analytics and UEBA
User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) uses machine learning (ML) to create a baseline of normal user and device behavior. It then detects anomalies that may signal threats such as compromised accounts or insider attacks. By analyzing both contextual and behavioral data, UEBA finds suspicious activity that traditional rule-based systems may miss and enables faster, more accurate and proactive threat detection.
Rise of Cloud Native AI Solutions
Cloud-Native AI Security, a next-generation strategy that blends AI, ML and scalable cloud infrastructure for proactive, automated protection, has grown in popularity as a result. For example, in March 2025, Accenture and CrowdStrike collaborated to modernize security operations by combining the AI-powered CrowdStrike Falcon platform with Accenture's security services. This allowed for real-time threat detection, prevention and response. Through partnerships, businesses can cut expenses, combine tools and optimize their SecOps workflow by up to 60%.
Shortage of Skilled Cyber Security Professionals
With the increasing number of cyber threats and the shortage of qualified personnel, cybersecurity becomes essential. AI improves defensive and attack capabilities. Over 4 million more cyber experts are needed worldwide, and 67% of organizations are experiencing moderate to critical skills gaps (World Economic Forum's Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025).

Challenges
·
Data Privacy Concerns
Large datasets, which frequently contain sensitive organizational or personal data, are the foundation of AI systems. Such datasets can present serious privacy risks, particularly in the event that models are cooperated. While improper data handling can violate regulatory standards like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), attackers may be able to reverse-engineer AI systems to extract sensitive information. AI systems must concurrently balance protecting sensitive data privacy with preserving performance, which is a tough and continuous task.
·
Emerging AI-Powered Attack Vectors
As
attackers increasingly use AI to create intelligent, adaptive and
difficult-to-detect threats, emerging AI-powered attack vectors present a
serious cybersecurity challenge. Traditional signature-based systems are
essentially rendered useless by these attacks, which can recognize
vulnerabilities, learn from defenses and exploit them instantly. Deep
fake-based social engineering, malware that evolves to evade antivirus
software, AI-driven phishing with customized messages, and intelligent botnets
that dynamically modify attack patterns are a few examples. Organizations must
embrace AI-enabled defenses with predictive threat analysis, behavioral
monitoring and automated response to keep up with the rapid pace of change. AI
improves cybersecurity, but it also gives attackers more power, which feeds the
ongoing arms race.
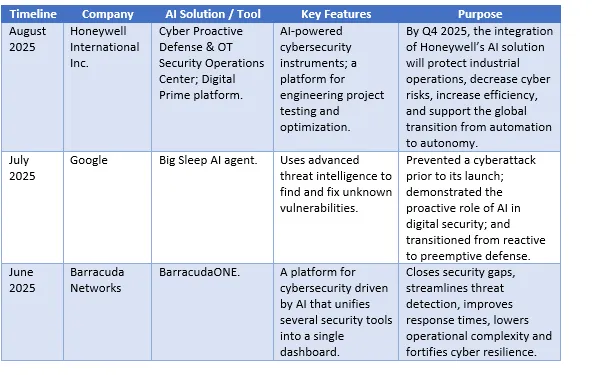
How Vendors are Advancing Cybersecurity Automation
Future Outlook
The future of AI in cybersecurity promises more advanced, proactive and automated defenses. Key developments to anticipate include:
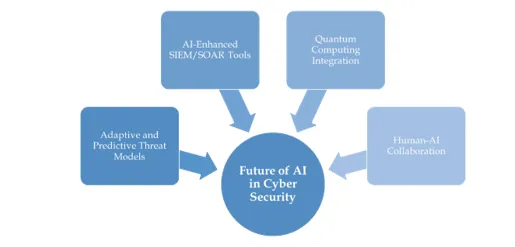
- AI-Powered SIEM/SOAR Instruments: AI will be used by next-generation security information and event management (SIEM) and security orchestration, automation and response (SOAR) solutions to both proactively detect threats and take appropriate action. Without human assistance, these systems will recognize irregularities, separate threats, modify defenses, assess vulnerabilities and even automatically apply patches.
- Quantum Computing Integration: AI-driven cybersecurity can be greatly improved by integrating quantum computing technologies. AI can detect sophisticated threats and spot complicated patterns in large datasets far more quickly than traditional systems by using the enormous processing power of quantum systems. This strengthens overall digital security by helping with quicker anomaly detection, real-time cyber-attack response and improved predictive capabilities.
- Human-AI Collaboration: Human-AI collaboration integrates human creativity, critical thinking and responsiveness with AI systems' data processing and automation capabilities. In industries like healthcare, customer service and the creative sector, this mutually beneficial partnership uses each party's strengths to solve challenging issues, innovate and boost productivity. When AI tools and algorithms are combined, human workers can concentrate on strategic tasks while AI takes care of repetitive or data-intensive tasks, which improves decision-making and productivity.
- Adaptive and Predictive Threat Models: AI's adaptive and predictive threat models change from reactive to proactive security by evaluating data, detecting anomalies and anticipating cyber-attacks using ML. While adaptive models continuously adapt to new data and changing threat scenarios, predictive models use historical data to predict future threats. This makes them strong to sophisticated and new attacks that traditional tools overlook, such as insider threats and zero-days.
Conclusion
The use of AI in cybersecurity is expected to grow significantly as industries deal with more complex cyber threats and altered attack methods. Businesses can proactively protect their digital assets with the improved threat detection of AI-driven solutions, real-time response capabilities and predictive analytics. It is impossible to misjudge the innovative potential of AI in encouraging cybersecurity frameworks, despite obstacles like high implementation costs, data privacy issues and adversarial attacks. The factors such as rapid adoption by countries across the globe, regulatory support, increasing investments in defensive AI and digital transformations can be counted as emerging trends.
AI is expected to become a crucial part of modern cybersecurity strategies as technology develops and is adopted by more industries. It will assure more intelligent and robust disobedience against new cyber threats. For organizations, AI is not just a transformative innovation for cybersecurity operations; it is becoming a crucial part of their mission statements.
Looking for Consulting & Advisory Projects
