Antihelminthic Drugs: Playing a Vital Role in Combating Parasitic Infections
January 19, 2026
In-depth market intelligence to support growth and planning.

Antihelminthic drug refers to medications designed to treat individuals afflicted with infections from parasitic worms, such as roundworms, tapeworms and flukes. These medications work by either disrupting the energy metabolism pathway or the neuromuscular function that causes worm paralysis or death, and ultimately, enabling the expulsion from the host. Common classes of antihelminthics important for both human and veterinary clinical practices include the benzimidazoles (albendazole, mebendazole), macrocyclic lactones (ivermectin), and praziquantel, each classified for different helminth species. Used across human and veterinary medicine, these antihelminthic drugs are critical in the global deworming programs that address the burden of neglected tropical diseases. Drug resistance to antihelminthic drugs and the development of new antihelminthic formulations are detrimental to the future of antihelminthic medications and are expected to be seriously considered moving forward.
The market for antihelminthic drugs encompasses the worldwide production and consumption of the medicines and drugs that effectively manage parasitic worm infections in humans and animals. With a high global burden of soil-transmitted helminthiasis and schistosomiasis, the market is expected to grow steadily in tandem with the expansion of public health programs in endemic areas. The market growth is further aided by nationwide mass drug administration (MDA) programs organized by organizations such as the WHO, along with increasing veterinary demand due to livestock management and pet health. The market is impacted by challenges, including increasing drug resistance, generic competition driving down drug prices, and the need to develop new formulations, which will guide future research and policy. The market is essential to the global health of the population, carefully managing the balance between large-scale low-cost supply and new knowledge or innovation to maintain long-term parasite control.
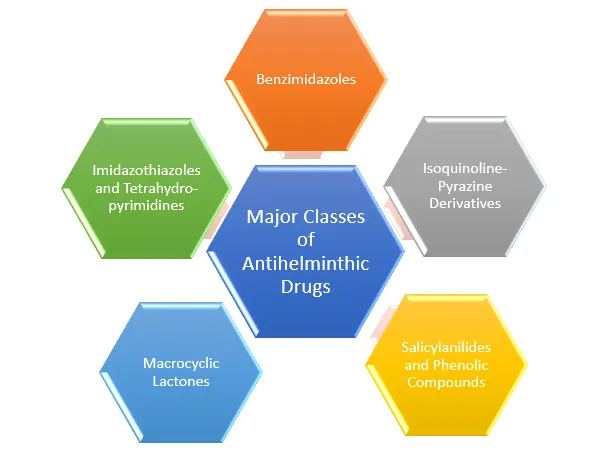
Major Classes of Antihelminthic Drugs and Their Mechanism of Action
Source: BCC Research
Benzimidazoles
Mechanism of Action: Inhibits microtubule formation, blocking glucose uptake. Effective against a wide range of nematodes, such as roundworms, whipworms and hookworms.
Examples: Albendazole, Mebendazole, Thiabendazole, Fenbendazole, Oxfendazole and Flubendazole.
Imidazothiazoles and Tetrahydropyrimidines
Mechanism of Action: Act as nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonists, causing spastic paralysis in worms.
Examples: Levamisole, Pyrantel pamoate, Tetramisole and Morantel tartrate.
Macrocyclic Lactones
Mechanism of Action: Open chloride channels, causing paralysis and death. They are widely used for applications in onchocerciasis, lymphatic filariasis and veterinary use.
Examples: Ivermectin, Moxidectin, Doramectin and Milbemycin oxime.
Salicylanilides and Phenolic Compounds
Mechanism of Action: Disrupts oxidative phosphorylation in tapeworms.
Examples: Niclosamide, Oxyclozanide, Closantel and Rafoxanide.
Isoquinoline-Pyrazine Derivatives
Mechanism of Action: Increases calcium ion permeability, leading to paralysis of flukes and tapeworms.
Examples: Praziquantel, Epsiprantel and Pyquiton.

Source: BCC Research
Innovative Pathways for Antihelminthic Drugs
Prevalence of Helminth Infections
Helminth infections continue to rank among the most common forms of parasitic diseases worldwide, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions where environmental sanitation and clean water access are limited. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that worldwide, more than 1.5 billion people are infected with soil-transmitted helminths. The extent of infection, particularly in children, underscores the need for extensive efforts to prevent infections through treatment programs, which increases the demand for antihelminthic drugs. Also, companies are focusing on targeting helminth infections. For example, in the 2024 annual report, the Drugs for Neglected Diseases initiative (DNDi) highlighted that infections from helminth (parasitic worm) diseases remain highly prevalent worldwide and are now a key target of their portfolio. In response, governments and non-governmental organizations are increasing deworming campaigns to reduce morbidity burden and improve overall health within communities, and therefore, the market continues to see significant demand for antihelminthic drugs.
Expansion of Public Health Initiatives and Mass Drug Administration (MDA) Programs
Public health interventions at the global and regional level, including WHO's "Deworm the World Initiative," UNICEF-supported campaigns and national programs, have built and sustained strong demand for antihelminthic medications worldwide. Also, in August 2025, Mankind Pharma, in partnership with the Lucknow Academy of Pediatrics (LAP), launched India’s largest de-worming awareness drive on National Deworming Day. Such programs supply and distribute mass quantities of medications for their targeted population at no charge or via a subsidized price. Consistently, pharmaceutical manufacturers, having the capacity to produce and distribute these medications, benefit from procurement agreements and consortia with organizations such as the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and World Bank, which provide long-term stability for market demand and provide, at times, significant financial support.
Growth in Veterinary and Livestock Sectors
The veterinary application of anti-parasitic drug treatment represents a rapidly expanding market. In livestock and companion animals, there is a rapidly increasing incidence of parasitic infections. Global meat, dairy and aquaculture production is on the rise. Therefore, economic impact, such as any losses resulting from infestations of helminths and other parasites, is a major concern. Also, increasing drug approvals for the treatment of helminth infections is boosting the growth of the veterinary and livestock sectors. For example, in September 2025, Zoetis announced that its product Dectomax‑CA1 Injectable (doramectin formulation) has received conditional approval from the U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA) for the prevention and treatment of the parasitic infestation caused by New World Screwworm (Cochliomyia hominivorax) in cattle. Hence, pet owners are becoming more involved in administering preventative deworming treatment and livestock producers are utilizing deworming treatment programs. This has led to new veterinary-specific formulations and combination products.
Increased Awareness and Preventive Healthcare Measures
An increase in public awareness of parasitic infections and their effect on health and economic productivity is motivating individuals and communities to seek consistent deworming treatment. Educational campaigns, school health programs and efforts by NGOs are creating potential for early identification and preventative care. For instance, in April 2025, the Irish Society for Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (ISPCA) partnered with Chanelle Pharma to run a nationwide pet parasite awareness campaign in Ireland, emphasizing the importance of regular flea and worm treatments for cats and dogs. The campaign included product donations (three months of treatment for shelter animals) and in-store promotions tied to the purchase of parasite-control products. Ongoing improvements in healthcare infrastructure and diagnostics in developing economies are also supporting evidence for increased uptake of antihelminthic drugs.
Future outlook
The antihelminthic drugs market is projected to exhibit a growth trend, driven by steady global prevalence of parasitic infections, increased deworming programs, and their growing application in veterinary medicine. Drug development, including formulations such as sustained-release and combination therapies, will increase opportunities for innovation and collaboration, especially as the One Health model integrates human/animal health from a healthcare perspective. A continued commitment to R&D, policy support and more affordable options — balanced with effective interventions — will drive the market, given the potential for drug-resistant parasites, low profit margins in public health and access issues in low-resourced areas. The future of this market will depend on R&D, cost-effective options and a supply chain that meets the market needs.
Strategic Takeaways for Industry Leaders
It is critical for industry leaders to capitalize on innovation-led growth by developing next-generation antihelminthic drugs and combination formulations to combat the increasing risk of parasite resistance. Investments in R&D of drugs with new mechanisms of action, extended-release properties and broad-spectrum compounds will be essential to establish a differentiated offering in a generic marketplace. Opportunities exist for public-private partnerships through participation of government and NGO-led deworming programs to sustain demand. For instance, in July 2023, Bayer collaborated with Swiss TPH to clinically develop an active substance for treating humans infected with soil-transmitted helminths (STHs), such as whipworm (Trichuris trichiura) and hookworms (Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus). In the veterinary space, leaders can consider achieving better margins through diversification into livestock and companion animal healthcare by offering value-added formulations or preventive solutions. Factors such as the One Health perspective, the development of digital supply chains and online pharmacies, and the production of affordable drugs with local manufacturing will enhance industry reach and resilience to challenges. Maintaining competitiveness will depend on an ongoing balance of innovation, accessibility and operational capabilities of both human and animal healthcare.
Conclusion
Antihelminthic drugs market contributes significantly to global health initiatives focused on eliminating widespread parasitic infections affecting billions of humans and animals around the world. The market is bolstered by global programs dedicated to mass deworming, veterinary applications and an increased interest in preventive medicine, particularly within developing nations. The market faces a number of challenges, including drug resistance, low profitability and low access rates in lower-income regions, but new opportunities are emerging in the form of novel formulations of antihelminthic products, combination therapies and the application of the One Health approach. The industry's success will depend on sustained investment in R&D, partnerships across sectors and optimization of the supply chain for affordable, effective and sustainable products. The market is expected to experience moderate but meaningful growth driven by increasing global demand for improved sanitation, animal health and emerging infectious diseases.
Looking for Consulting & Advisory Projects
BCC Research Beacon 
