Direct-to-Cell (D2C) Satellite Communication Services: Bridging the World with Satellite Connectivity
Clear insight into competitor positioning and market share.

D2C satellite communication services refer to the type of communication that directly connects cellular devices to a satellite in space. This reduces the dependency on ground-based infrastructure and provides reliable connectivity even in far-off places. This technology is gaining preference as it plays a crucial role in enabling communication in rural areas, disaster-struck regions and other remote locations where it is difficult to set up a traditional network infrastructure.
It also offers support in critical use cases, including maritime and aviation communications, defense applications, and emergency support situations. As low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite constellations continue to grow, D2C satellite communication services are expected to offer improved data speed, reduced latency and more accessible global connectivity. In June 2025, Kyivstar announced that it had received approval for testing Starlink’s D2C satellite communication services. The motive behind this testing was to ensure that subscribers connect to the satellite using long-term evolution (LTE)-supported devices without the need for specialized devices.

Source: BCC Research
Understanding Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) Satellite Communication: How It Works
With D2C satellite communication services, satellites are usually treated as space-based cell towers. These new LEO satellites are equipped with antennas and software that support the operation of 4G/5G protocols, instead of the traditional relaying of signals between ground stations. Since the phones are directly connected to satellites, they can connect and receive the necessary connectivity without the need for any specialized hardware.
The satellite transmits the signal to ground stations, which pass it through the mobile operator’s network to the internet or other device or cell. Throughout this process, the user doesn’t feel any difference except in the background. The signal for their devices is routed through the space instead of any tower on the ground. The D2C satellite communication services are currently available for messaging and any emergency alerts. However, services such as voice calls and internet services are also expected to be made available in the coming years.
Why D2C Satellite Communication Stands Out?
- Global Coverage: In addition to providing smooth services in the regular environment and territory, the D2C satellite communication service also provides seamless communication support in hard-to-reach areas and difficult terrains, where setting up the network infrastructure is difficult.
- Low Latency: These services use the LEO satellites, which orbit closer to the Earth than the geostationary satellites. This shortened distance helps reduce the signal travel time, thus resulting in lower signal delays.
- Emergency Support: This communication technology ensures that the connection is not affected by situations of power or tower failure, maintenance or natural disasters such as floods and tsunamis. This helps ensure the smooth provision of the network at such critical times.
- Supports IoT Applications: The D2C satellite communication can be integrated with IoT devices, used in agriculture, environmental monitoring, fleet management and logistics activities, thus ensuring control and timely actions.
Evolution of Satellite Communication:
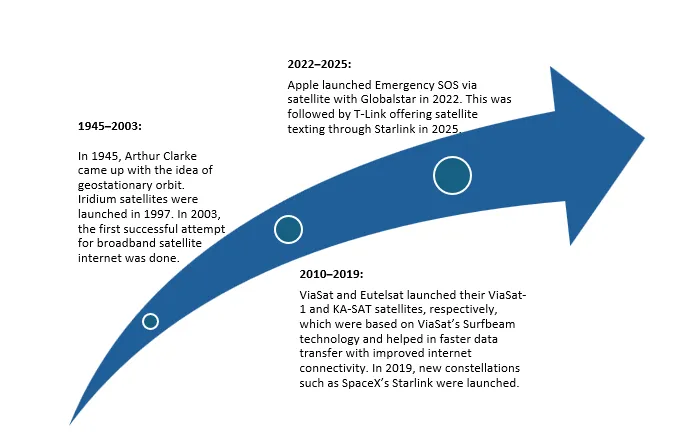
Source: BCC Research
1945–2003: In 1945, Arthur Clarke came up with a geostationary orbit, which is now called the “Clarke Orbit”, hosting around 500 satellites by 2021 for global communications. Later, engineers from Motorola came up with Iridium, which is the first global satellite network, and these satellites were officially launched in 1997. In 2003, the first successful attempt for broadband satellite internet was made by EUTELSAT, and it was called the e-BIRD satellite.
2010–2019: In 2010, ViaSat and Eutelsat launched their ViaSat-1 and KA-SAT satellites, respectively. These satellites were based on ViaSat’s Surfbeam technology, which helped speed up data transfer and improve internet connectivity. Later in 2019, new constellations such as SpaceX’s Starlink were launched.
2022–2025: Apple, with the help of Globalstar, launched Emergency SOS via satellite in 2022, followed by T-Link offering satellite-based texting through the Starlink network in 2025. T-Mobile announced that in October 2025, it will provide data connectivity through its Starlink-backed satellite-to-cell service. In addition to texting, picture and audio clip sharing, this satellite will also support the functioning of third-party apps when out of terrestrial range.
Applications of D2C Satellite Communication Services:
|
Application |
Description |
|
Emergency and
Disaster Response |
This
communication system is necessary during events, such as floods and
earthquakes, as network towers usually get destroyed during such events. |
|
Remote and Rural Connectivity |
D2C satellite communication services help provide
network coverage and connectivity in remote and hard-to-reach locations such
as mountains and remote villages. |
|
Agriculture |
Farmers are
increasingly adopting this technology to monitor and receive updates on soil
and crop health, and weather updates or forecasts. |
|
Maritime and Aviation |
This technology is used to monitor fleets of ships,
planes and offshore platforms, where obtaining a stable connection for
communication or monitoring is usually difficult. |
|
Military and
Defense |
D2C satellite
communication services help support communication in remote and hostile
areas, where traditional methods are risky. |
Source: BCC Research
Key Growth Levers to Boost D2C Satellite Communication Services Adoption:
Rising demand for global connectivity: With the rising demand for internet penetration, the need for stable connectivity in remote areas has been increasing. Thus, the requirements for seamless connectivity for business, personal and other such functions reflect a growing trend.
Advancement in satellite technology: LEO has been developed and is increasingly being considered for use as it supports lower latency, provides high-speed data and has greater capacity than other geostationary satellites (GEO) used traditionally. These improvements are thus pushing more innovators and service providers to adopt these services, and thus offer advanced communication services such as D2C satellite communication services.
Reducing launch and manufacturing costs: With the introduction of miniature satellite designs and the rising production of satellites, the costs have been falling. Though the prices are still high, improvements in manufacturing technology have reduced these costs. Also, with growing dependence on satellites for functions such as communication, navigation, defense and security, the demand for satellites is expected to grow, which is further expected to result in reduced manufacturing and launch infrastructure costs.
In May 2025, South Korea granted regulatory approval for SpaceX’s Starlink and Eutelsat’s Oneweb to provide LEO satellite internet services. This approval will provide low-latency, high-speed internet services in rural areas, aviation, maritime sectors and other traditional network areas.
Barriers on the Path to Expansion of D2C Satellite Communication Services:
Infrastructure and Set-up Cost: Although D2C satellite communication service can effectively run on existing network infrastructure, making, launching and maintaining the satellite can be expensive, thus affecting its wider adoption.
Weather and Environmental Factors: Weather conditions, including cloudy conditions, rain, and line of sight issues, can impact the services, especially for higher frequency bands. Thus, providing steady and stable connectivity constantly in such conditions is a challenge at present.
Limited Bandwidth: The satellite communication system is equipped with limited bandwidth. Thus, the speed can be affected in case of heavy usage or a large number of people accessing the network at the same time.
Future Outlook and Conclusion
The D2C satellite communication service is still in its early developmental phase, but is expected to provide a promising growth trajectory in the coming years, driven by ongoing improvements in technology and enhancements in regulatory support. In the coming years, this service is expected to grow significantly, backed by improvements in its offerings, such as improved IoT connectivity, voice communication, and other related satellite-based services. Also, with improvements in signal processing, antenna designs and other associated components, the adoption rate of this satellite service is expected to improve further. With stringent policies being adopted for service provision and privacy, the demand for these services is expected to grow at a rapid pace in the coming years.
The D2C satellite communication service has a huge growth potential in the coming years by providing a seamless global connectivity option. With its feature of directly connecting smartphones to satellites, it can help improve the connectivity over larger areas, and also support emerging contact services. Though the technology is in its initial stage and faces challenges such as cost and regulatory requirements, in the coming years, with a growing adoption rate and improvements in technology, these issues can be overcome, thus ensuring its smooth operation and usage.
Looking for Consulting & Advisory Projects
