Electric Vertical Take-Off and Landing (eVTOL) Aircraft: Redefining the Future of Urban Air Mobility
In-depth market intelligence to support growth and planning.

Electric vertical take-off and landing (eVTOL) aircraft refer to a new type of drone designed to carry passengers. These aircraft use multiple electric motors and rotors to gain the lift needed and propulsion. These are completely dependent on electric power for their operation, making them attractive as a sustainable mode of transport. These vehicles are gaining preference for their features, including reduced noise and environmental pollution, the ability to fly efficiently both with a pilot or autonomously and the use of electric propulsion.
Additionally, these aircraft can take off and land vertically in limited space, unlike traditional aircraft and helicopters, which need a considerable dedicated space for operation. The demand for eVTOL is expanding, driven by the urgent need for sustainable and efficient urban transport solutions. eVTOLs are a new class of electric aircraft designed to provide a quiet, zero-emission alternative to ground-based transportation, poised to revolutionize urban and regional mobility.
Evolution of eVTOL: From Concept to Reality
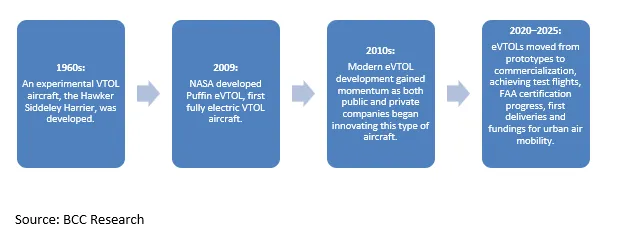
The journey of eVTOLs has grown significantly from concept to the commercialization stage and regulatory certification. Though the VTOL technology existed since the 1960s, the first eVTOL was launched in 2009 by NASA and the model was called Puffin eVTOL. Later, in the 2010s, private companies, including Joby Aviation and Volocopter, innovated and developed eVTOLs for various purposes, such as emergency medical support and traffic management.
In February 2025, ICATT and The ePlane Company entered into an agreement. The ePlane Company will manufacture 788 eVTOL air ambulances for the International Critical Air Transfer Team (ICATT). These air ambulances are designed to carry a patient, a paramedic, a pilot and a stretcher, along with other necessary life-saving medical equipment.
This shift is driven by advancements in factors such as energy density, flight control systems and electric propulsion. The industry is now adopting lift-plus-cruise designs for long-range travel. Furthermore, clear regulatory guidelines from agencies, including the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in the U.S. and the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA), are also driving support for innovation, development and commercial adoption of eVTOLs.
Key Enablers Powering eVTOL Growth
The growth of eVTOLs is supported by various factors, such as technological advancements, urban mobility challenges and faster transportation options. These features, along with increased investments in this sector, are expected to drive the growth of these transportation models.
Urban Congestion and Demand for Faster Travel: With a growing urban population, traffic congestion has become a major challenge, leading to longer commute times. eVTOLs offer a transformative solution by providing point-to-point travel, bypassing road infrastructure and drastically reducing travel times. In June 2022, Ehang’s pilotless eVTOL, EH216-S, completed its first human-carrying flight successfully in Indonesia. This autonomous aircraft can carry two passengers, covering a distance of 30 kilometers, with a top speed of approximately 130 kilometers per hour. The country’s Department of Transportation is thus considering its use to ease traffic congestion.
Decarbonization and Sustainability Goals: The global push for zero-emission transportation has propelled the adoption of electric aviation. eVTOLs, powered by electricity, produce zero in-flight emissions, aligning with long-term climate goals and corporate net-zero mandates.
Technological Advancements: Continuous improvements in battery energy density, electric propulsion systems and autonomous flight technology are making eVTOLs more viable and appealing. Innovations in battery technology are enhancing the range and efficiency of these aircraft, making them practical for a wider range of applications. In June 2025, Gotion High-tech announced that the company would be providing 46-series cylindrical battery cells for the Ehang EH216 eVTOLs. These are high-power lithium batteries, especially designed for eVTOLs, and will offer high-energy density. These batteries also have fast-charging capabilities, with the ability to reach 80% of charge in 18 minutes, and certain advanced batteries provide a 10-minute charging time.
Strong Investment and Cross-Industry Collaboration: The industry is fueled by strong investments from major aerospace companies, automotive firms and venture capital firms. Collaborations with airlines, airports and city authorities are building the foundational ecosystem for real-world deployment. For example, in July 2025, Ehang Holdings Ltd. and Reignwood Aviation Group entered into a partnership with the aim of expanding the eVTOL services in China and Southeast Asia. The companies are also planning to develop their digital fleet management platform, with the aim of managing high-density, high-frequency and low-altitude drones and eVTOL operations.
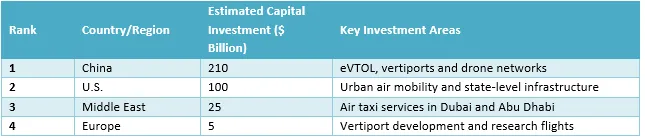
The table below shows key capital investment by country in the low-altitude economy as of 2025:
Barriers to eVTOL Adoption
eVTOLs hold a promising future for the urban mobility sector in the coming years; however, certain challenges need to be tackled that might hinder the large-scale adoption of these devices. Some of the significant challenges around cost, regulatory requirements and others are mentioned as follows:
Regulatory Hurdles and Certification Delays: The foremost challenge remains the complex and stringent regulatory process. Certification delays can significantly increase costs and push back commercialization timelines.
High Development and Infrastructure Costs: The upfront costs, which include the initial cost for manufacturing, obtaining licenses and certifications for eVTOLs, and costs required for building the necessary ground infrastructure, such as "vertiports" and charging stations, are substantial. These high capital expenditures pose a significant financial barrier to widespread adoption.
Public Acceptance and Safety Concerns: Gaining public trust is a major hurdle. Concerns about safety, noise pollution and the crash risk of these new aircraft could slow the adoption of eVTOLs without rigorous safety testing and transparent communication. Although most designs are quieter than helicopters, public perception remains a key challenge.
Airspace Management and Supply Chain Resilience: Safely managing the increased air traffic in urban environments requires new air traffic control technologies. Additionally, the supply chain for key components, particularly lithium for batteries, presents a significant bottleneck.
Strategic Initiatives of Leading Companies in the eVTOL Industry

Source: BCC Research
Future Outlook and Expected Adoption Trajectory
The adoption of eVTOLs is expected to showcase structured and strategic growth. Commercial use of eVTOLs is expected to begin in select cities, such as Dubai, in 2026, followed by Saudi Arabia, Japan, and other cities planning to launch in the coming years. This growing adoption is thus expected to transform urban transportation in the future.
Following this, the eVTOL aircraft will enter a scale-up phase, as major companies such as Joby and Archer ramp up production and expand their operational routes from a few select cities to a wider network. In June 2025, Archer Aviation started test flights of its Midnight eVTOLs in Salinas, reaching a height of 1,500 feet with a speed of approximately 125 miles per hour. The company plans to launch its commercial air taxi services in Southern California, U.S., by early 2026. The eVTOL is designed to carry four passengers plus a pilot, capable of traveling up to 150 miles per hour and featuring a design that allows for back-to-back flights with a faster battery charging time.
By 2035, the industry is expected to achieve "mass adoption," with forecasts suggesting tens of thousands of air taxis in use worldwide. This phase will be characterized by the integration of eVTOLs into the broader multimodal transportation ecosystem. To get there, the industry must overcome key hurdles, including achieving full autonomy to reduce pilot costs, developing robust and scalable vertiport networks in dense urban areas, and successfully integrating new aircraft into existing air traffic management systems. As these challenges are addressed, eVTOL is poised to transform urban life by offering a faster, more sustainable and efficient mode of transportation, fundamentally reshaping how people and goods move in the 21st century.
Looking for Consulting & Advisory Projects
