Ethernet Traffic Generators: The Backbone of Ultra-High-Speed Networks in the AI and 6G Era
Forecast-backed insights for confident investment decisions.

An Ethernet traffic generator is a software or hybrid tool that creates and injects artificial network traffic to test switches, routers and other networking equipment. Next-generation generators will dynamically adapt to accommodate shifting network circumstances, transmitting packets of different sizes, protocols and speeds. Through programmability, automation and analytics based on artificial intelligence, these systems will offer real-time insights, forecast failure and optimize performance. The development enables ongoing verification under realistic and stressful conditions, ensuring that the design is resilient in high-speed networks.
Nowadays, Ethernet traffic generators are vital as networks grow faster, denser and more sophisticated with the advent of cloud computing, AI, edge computing, 5G/6G and industrial IoT. Untested devices moved into production may encounter bottlenecks, packet loss, jitter, or system crashes, and be exposed to compatibility issues. Traffic generators mimic actual conditions, so engineers can test latency, throughput, frame loss and jitter precisely. The main benefit is identifying weaknesses early, ensuring smooth device performance for end users.
Looking ahead, traffic generators will become indispensable in certifying that infrastructure meets demanding service level agreements (SLAs) and can scale without failure, as networks evolve to support ultra-high data rates (e.g., 800 Gbps, 1.6 Tbps), deterministic services, holographic or immersive experiences, and extreme reliability.
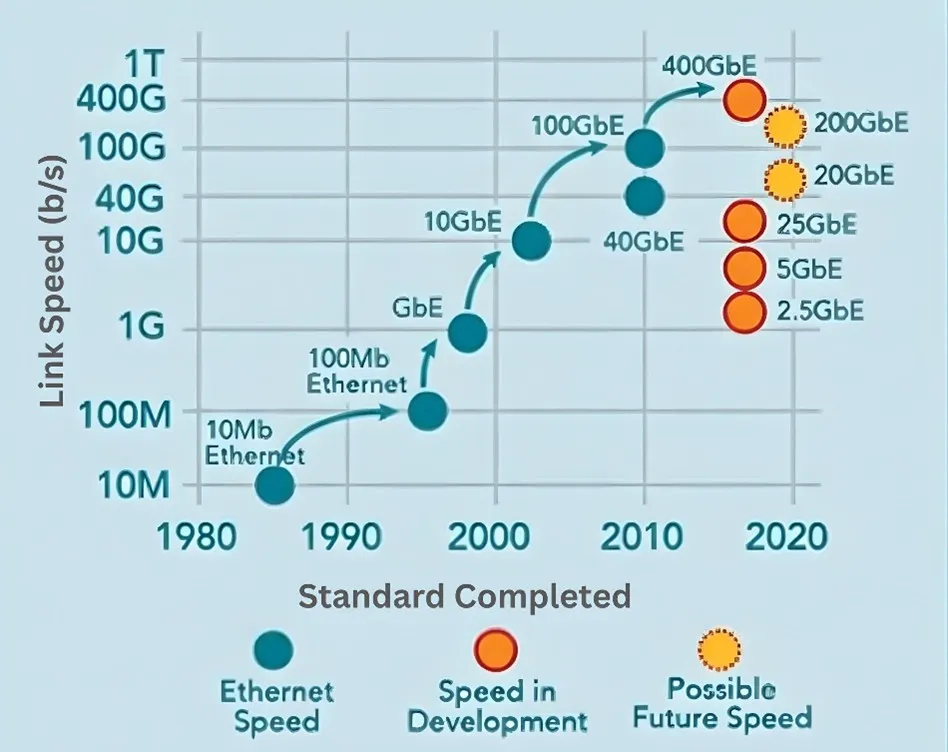
Source: Ethernet Alliance 2025
The diagram above shows how new Ethernet speeds are being introduced faster than ever. The gap between standard approval and product launch is shrinking, but supporting higher speeds has become more complex. With PAM4 signaling at 400GE and beyond, testing becomes more challenging as end users now demand reliability and performance that exceed standard requirements.
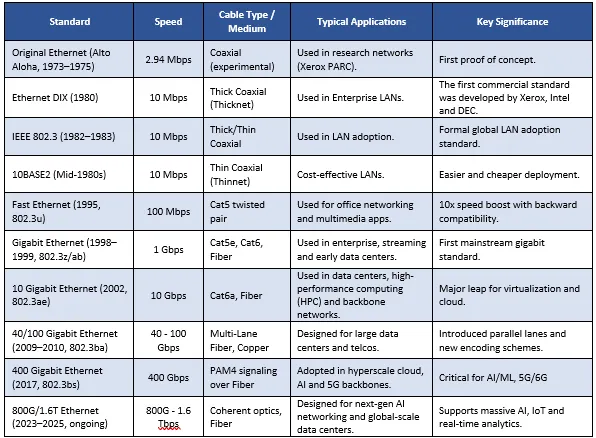
Evolution of Ethernet Standards
The history of Ethernet is a testament to an incredible path from local network test beds to the foundation of the current AI-fueled, high-speed data backbone. Over the course of more than five decades, Ethernet standards have evolved from 2.94 Mbps research networks to the latest 800G and emerging 1.6 Tbps technologies. With each new generation, there has been an increase in speed, new cabling media and added capabilities to address changing demands in enterprise, data center and cloud applications. The table given below follows this progression, comparing major Ethernet milestones, their technical specifics, uses and primary network innovation contributions.
Evolution of Ethernet Standards
Key Drivers Accelerating Adoption of Ethernet Traffic Generators
There are several forces that are driving wider adoption, particularly through aligned policies, supportive ecosystems and robust infrastructure. Some of them are mentioned below.
- Government and Public Sector Investment in High-Speed Infrastructure: Numerous nation-level broadband and next-generation network initiatives, such as Digital India, Europe's Next Generation Internet, and the U.S. Networks of the Future, include plans to expand fiber, 5G/6G and edge infrastructures, resulting in a growing need for traffic generators to certify and test network components.
- R&D Funding and Standards Bodies Requirements: Standards bodies such as the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) require conformance, interoperability and performance testing, so traffic generation tools are an essential part of test facilities. Similarly, government investments in 5G and 6G development typically require proof of test infrastructure, including traffic generators. For example, the U.S. framework of 5G testing explicitly asserts that testing infrastructure is the key to enabling advanced 5G deployment.
- Surge in Data Volumes and Network Complexity: With the advent of AI, video streaming, AR/VR, autonomous systems and large-scale IoT, the networks need to support diverse, bursty and unpredictable traffic. Therefore, it becomes crucial to stress-test devices and infrastructure with synthetic traffic. Reflecting this increasing need, India's AI infrastructure projects indicate that the government has sanctioned around ₹107.3 billion (approximately $1.24 billion) for AI-oriented data center infrastructure, suggesting an acceleration in data and compute needs.
- Ecosystem Pressures and Competitive Differentiation: Switch, router and NIC vendors distinguish themselves on performance, underload stability and low-latency grounds, employing sophisticated traffic generation as a demonstration point. The test and measurement community, including vendors like Spirent, also competes to provide greater throughput, more programmability, and more affordable solutions that support these performance levels.
Applications Across Diverse Real-World Industries
- Telecom and datacom industries utilize Ethernet traffic generators to validate the performance and reliability of switches, routers, optical transceivers and network interface cards under operation as required in actual real-world traffic conditions.
- Cloud and AI infrastructure providers utilize the generators to stress-test interconnect fabrics and evaluate system performance under high-bandwidth and saturation scenarios.
- Government and defense laboratories utilize Ethernet Traffic Generators to confirm secure communication systems and determine the robustness of new networking architectures.
These advances signal developments that indicate that the future of Ethernet traffic generation is moving closer to the data plane, integrating richer analytics and embedded test capabilities for more intelligent and seamless network validation.
Technological Developments in Ethernet Traffic Generators
Given below are some notable advances of 2025 showcasing how various companies or research entities are pushing the envelope:
• High-Speed Terabit Generation: Teledyne LeCroy’s Xena Z1608 Edun Ethernet Traffic Generator is designed to deliver up to 1.6 Tbps of traffic that supports 100GE, 200GE, 400GE, 800GE and 1.6TE speeds for end-to-end verification of the next-generation AI/ML-driven networking infrastructure.
• Programmable and P4-Based Traffic Generators: Programmable and P4-based Ethernet traffic generators represent a new paradigm in network testing. The P4TG project implements a traffic generator directly onto a programmable data plane (Intel Tofino ASIC) using the P4 language. It makes it possible to produce several 100G+ Ethernet streams and supports flexible encapsulation types, such as VLAN, VXLAN and MPLS. Future Ethernet traffic generation will be integrated directly into programmable switches and ASICs, eliminating the need for external tools and enabling smarter, more integrated network testing.
Future Outlook
Over the next five to 10 years, Ethernet Traffic Generators will evolve to support multi-terabit speeds (3.2–6.4 Tbps) and accommodate diverse media, such as optical and co-packaged optics. They will be integrated into switches and routers for in-band testing and real-time monitoring. With P4 programmability and AI automation, these tools will facilitate adaptive, self-optimizing network validation. The future goes beyond simply higher speeds to embrace smarter, embedded and comprehensive testing capabilities.
Looking for Consulting & Advisory Projects
