GenAI in the Lab: Accelerating Drug Discovery Through Generative Molecular Design
January 20, 2026
Tailored research built around your exact strategic priorities.

GenAI in the Lab: Accelerating Drug Discovery Through Generative Molecular Design
The process of drug invention has long been slow, difficult and costly, relying largely on trial and error. Time, expense and complexity have hindered success. GenAI is offering science a new creative partner, one who can do it with great accuracy, speed and intention. Instead of sifting through millions of compounds, scientists can now digitally design new chemical structures, tailoring them to disease targets even before they reach a test tube.
This change heralds an era of intelligent molecular design, where computation, not chance, drives discovery. Algorithms trained on enormous chemical and biological data sets are beginning to devise a plan to create new drug chemicals that may have never existed in nature. By combining human insight with machine creativity, GenAI is revolutionizing pharmaceutical research from a slow process to a vibrant collaboration between data and discovery.
Source: BCC Research
Emerging Trends in AI-Driven Drug Discovery
GenAI is transforming drug discovery to be more predictive, creative and accurate. Instead of manually screening millions of compounds, scientists now have the power of AI models to design molecules that are the best fit for a biologic target, thus significantly shortening the time taken to go from concept to candidate. This replacement of blind trial-and-error with intelligent molecular design is giving researchers the ability to delve into virtually unlimited chemical spaces, most of which were previously inaccessible. AI-driven platforms, in fact, are not just speeding up the process but also fundamentally changing the way innovations are conceived by suggesting compounds that a human chemist may never have thought of.
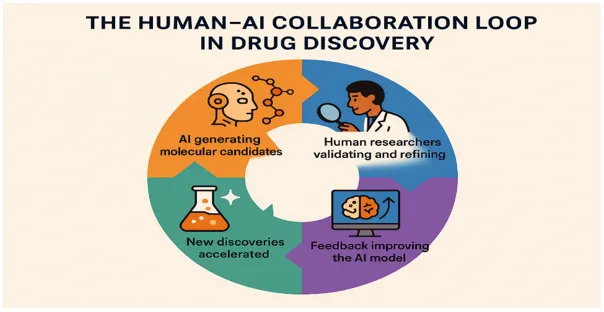
A key trend is the use of AI combined with laboratory automation and computational simulation to form a closed-loop system in which algorithms design molecules, automated labs test them, and real-time feedback refines future designs. As AI systems advance, they become autonomous discovery partners, reasoning, inventing and adapting. This marks a new era of drug innovation where AI enhances, but does not supersede human creativity.
Source: BCC Research
Strategic Alliances Driving the GenAI Revolution
GenAI is a significant factor in the transformation of drug discovery in the pharmaceutical industry. The top pharma companies are collaborating with AI companies to leverage the forces of biology and AI design simultaneously. For instance, in December 2023, Absci collaborated with AstraZeneca to demonstrate the role of generative protein design in the rapid discovery of new antibodies. The formation of such partnerships signals a significant shift in the way the industry is moving. At the center of this change is the interaction between computation and biology. By collaborating on knowledge, data and algorithms, these partnerships evolve into a shared ecosystem where R&D is redefined, and AI, combined with human insight, becomes a co-creator of the next generation of drugs.
In June 2025, NVIDIA Corp. announced a strategic collaboration with Novo Nordisk to change the way drug discovery is done with the help of advanced AI infrastructure. As a part of the collaboration, the company will deploy NVIDIA's genAI platforms, simulation tools and the Gefion supercomputer to enable Novo Nordisk scientists to engineer highly personalized models and simulation scenarios for the genesis of molecule development and prediction. By leveraging high-performance computing and large-scale biomedical data, the partnership marks a departure from merely performing isolated drug-discovery experiments toward creating a fast, tech-driven ecosystem for therapeutic innovation.
Challenges on the Path Ahead
Despite technical advances, genAI in drug discovery faces significant moral, judicial and legal challenges. One of the major barriers is related to the quality and variety of data. AI models necessitate extensive datasets that depict chemical and biological interactions. However, a significant number of these are either incomplete, biased or not standardized. The absence of toxicity data, scarcity of negative results and lack of standardization may affect the results of predictive models and, consequently, molecular designs. Ensuring that AI-designed molecules are both efficient and safe will be possible if more accurate and transparent chemical datasets are available.
More essential is the problem associated with transferring the success achieved in a virtual environment to laboratory chemistry. Many AI-generated molecules are reported to have good results in silico, but they fail when tested in the laboratory. For example, a study published by the National Library of Medicine in August 2025 found that generative models could, in principle, produce promising drug candidates for targets such as CDK2 and KRAS. However, most of the molecules were either difficult to synthesize or biologically inactive when tested experimentally. This underscores that the relationship between algorithmic creativity and chemical viability remains complex and uncertain.
In addition to technical limitations, the debate on using GenAI in drug discovery is also influenced by ethical and safety aspects. One concern is that genAI may design molecules with harmful or toxic characteristics, underscoring the need for strict governing rules and responsible innovation practices. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s 2024 draft guidance on AI and machine learning in drug development requires algorithms to meet conditions of transparency, explainability and continuous validation — ensuring they are accountable, interpretable and trustworthy. In addition, issues of data privacy and intellectual property rights remain complex and are becoming more so as AI develops new molecular structures that may not be easily patentable.
Future Outlook: The Road Ahead
The future of drug discovery will depend on the deep integration of computation, automation and biology, driven by the continuing evolution of genAI. The future brought to us by a combination of on-demand modeling, robotic synthesis and predictive analytics will be one of closed-loop discovery, where AI fabricates molecules, labs with automation verify them, and feedback immediately updates the next designs. For instance, in October 2025, Nabla Bio Inc entered into a collaboration with Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited to deploy Nabla’s AI platform, the Joint Atomic Model (JAM), to design protein-based therapeutics, accelerating discovery-to-lab testing cycles to just three to four weeks.
This change pushes the limits of pharma innovation. Shifting toward AI-driven research environments will not only speed up the change but also make it safer and more creative. Researchers, to a large extent, will be responsible for interpreting AI findings and guiding the models with logical and moral supervision. Generative molecular design is not only transforming the drug discovery process but is also fundamentally changing the conception of intelligence, innovation and human health. In future, labs will become integrated ecosystems where algorithms and scientists collaborate continuously, creating not only the tools for medicine but also the medicines themselves.
Conclusion
GenAI is not only a lab tool, but also the next frontier of innovative science. GenAI, by combining data-driven intelligence with human creativity, is profoundly altering the methods with which we think, create and produce new drugs. Challenges remain, but the path is clear. Future laboratories will be powered as much by algorithms as by scientists united in purpose, creativity and discovery.
During this transition, the scientists' role will shift from mere data collectors to data interpreters who will guide AI to achieve innovations that matter. The collaboration of machine accuracy with human inquisitiveness is what will characterize the next decade of pharmaceutical breakthroughs. In this new model, faster is safer, and creativity will not be constrained by the limitations of chemistry.
On the contrary, genAI in drug discovery has brought a technological evolution and a radical change in the way we understand biology, disease and even possibility. The integration of computation and compassion is paving the way for a world where life-saving therapies are not discovered by chance but are designed through collaboration between humans and AI.
Looking for Consulting & Advisory Projects
BCC Research Beacon 
