Green Nanotechnology Market
Tailored research built around your exact strategic priorities.

Green nanotechnology is a branch of green technology that utilizes eco-friendly techniques to produce nanoparticles. By prioritizing renewable resources, it emphasizes the use of sustainable materials and focuses on reducing energy and material demand. Green nanotechnology is based on the principles of green chemistry and nanotechnology. It features cost-effectiveness, safety, and eco-friendliness. Various plant tissues, including leaves, stems, bark, seeds, roots, fruits and flowers, are extensively used for synthesizing nanoparticles. Green nanomaterials find applications in the food and textile industries, various biotechnological sectors such as biology and medicine, agriculture and wastewater treatment.
Figure 1: Illustration of
features of green nanotechnology
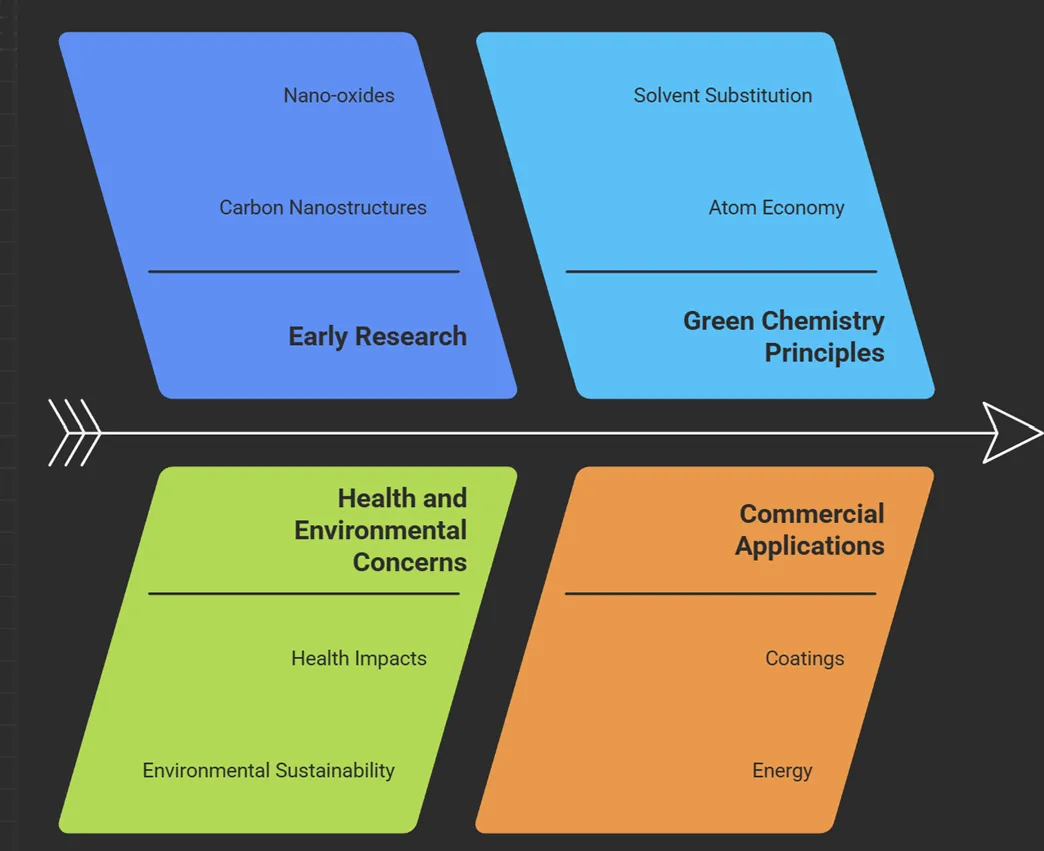
Figure 2: Advancement of
green nanotechnology
Early research in the 2000s focused on the remarkable properties of carbon nanostructures, nano‑oxides and nanocellulose. As the nanomaterials field matured, both health and environmental considerations gained popularity. Green chemistry principles began informing nanomaterial synthesis: atom economy, solvent substitution, catalysis and the use of safer reagents. Commercial traction followed in coatings (anti‑microbial, anti‑corrosion and self‑cleaning), energy (thin‑film photovoltaics, nano‑enabled batteries and electrolyzers), water (membranes and adsorbents) and packaging (barrier layers utilizing nanoclays and cellulose).
Current Market Scenario
Green nanotechnology facilitates water resource management and environmental remediation by providing advanced techniques such as photocatalysis and nano-bioremediation, among others. According to the European Commission, the Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation (ESPR) took effect in July 2024. It is the foundation of the Commission's strategy for circular and eco-friendly products. The regulation drives demand for green nanotechnology by promoting sustainable and recyclable product designs. This law encourages firms to utilize advanced nanomaterials to enhance energy efficiency and environmental performance. Green nanotechnology offers substantial remedies for controlling and reducing air pollution. Air streams using catalysts and filters produced from nanomaterials assist in the effective removal of pollutants, including particulate matter, nitrogen oxides (NOx), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Utilizing nanomaterials and nanodevices in green nanotechnology addresses the concerns related to food security and ecological balance. Green nanotechnology enables pesticides and fertilizers to effectively reach their target sites, thereby enabling the precise delivery of agrochemicals. The encapsulation of insecticides and fertilizers, and their gradual release in response to specific nanocarriers or nanocapsules, can increase nutrient absorption by plants while reducing runoff into water bodies.

Figure 3: Representation of green nanotechnology applications
Drivers and Restraints
Green nanotechnology is gaining traction as it addresses concerns related to eco-friendly agriculture, green energy and water treatment. Green nanotechnology aims to achieve the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). In the agricultural sector, nanotechnology enhances the efficacy of pesticides and fertilizers, aligning with SDG 2, specifically Zero Hunger, one of the 17 United Nations SDGs. It also aims to achieve SDG 7, specifically Affordable and Clean Energy in the energy sector, thereby helping to improve energy conversion and storage systems.
It contributes to SDG 15, which focuses on terrestrial ecosystem preservation, SDG 14, which emphasizes marine environment protection, and SDG 13, which prioritizes climate action. It helps promote clean production techniques and reduce waste, thereby encouraging SDG 12, which is responsible for sustainable consumption and production. However, when not properly managed, certain nanomaterials pose potential risks to ecosystems and human health. The high costs associated with green nanomaterials production are likely to restrain the growth of the green nanotechnology market.
Research and Development
Researchers are currently developing green synthesis techniques, including the study of plant-mediated nanoparticle production. This is due to a surge in demand for sustainable and eco-friendly alternatives. These plant extracts can serve as stabilizing and reducing agents, thereby opening up new opportunities for the environmentally friendly and cost-effective development of nanoparticles with enhanced size uniformity and stability. Green nanoparticles derived from plants are becoming highly promising for healthcare applications due to their superior pharmacological, nanodimensional and biocompatibility properties.
Future Outlook
Nanomaterials such as metal oxides, nanocarbons and nanocomposites help produce more efficient supercapacitors, batteries, and fuel cells with greater energy capacity. Also, by applying nanocoatings, green technology enhances energy efficiency by reducing friction and thermal insulation coatings to limit heat transfer. The integration of nanotubes into building materials offers a potential scope for the construction sector. Improvements in manufacturing processes, including continuous chemical vapor deposition methods and sustainable production methods, are expected to enhance the nanotube supply and reduce costs for construction applications.
According to a report from Ember, renewable power sources generated a 49% increase over the previous record of 577 terawatt-hours in 2022, reaching 858 terawatt-hours in 2024. Solar power production worldwide has doubled over the last three years, reaching more than 2,000 TWh in 2024. This growth was attributed to a surge in solar power generation.
Green nanotechnology helps mitigate environmental impact by employing innovative methods to enhance energy conversion, storage and utilization. It improves the performance of solar cells through nanomaterials such as nanowires, perovskites and others. These materials enhance power conversion efficiency, reduce manufacturing costs and facilitate the development of lightweight and transparent solar cells. For example, nanostructured perovskites, a revolutionary development in solar cell technology, have the potential to significantly enhance both stability and power conversion efficiency. Scientists are optimizing nanomaterials and thereby enhancing light absorption and reducing recombination losses, ultimately contributing to enhanced energy efficiency.
Looking for Consulting & Advisory Projects
