The Future of Secure Computing: Why Homomorphic Encryption Matters?
Clear insight into competitor positioning and market share.

Data is one of the most precious commodities at the beginning of this third millennium. Digitization has opened new doors in every area of business, and simultaneously, it has intensified market competition. In such a condition, we must consider stringent solutions for streaming and data loss. Older methods protect sensitive data once it is stored either on a physical or cloud server, but an emerging challenge lies in processing that data in the cloud while maintaining its encryption.
Homomorphic encryption (HE) allows calculations to be transformed into encrypted data, meaning that the calculations can be done without first decrypting the data. Thus, it lets organizations use cloud computing platforms for real-time data processing while protecting sensitive information. With rapid advancement in computing and artificial intelligence (AI) today, HE can be part of an automated system, where customized system-agnostic models securely and efficiently process data according to the specific requirements of an institution.
What's Powering, Slowing and Shaping the Future of Homomorphic Encryption?
The use of HE is being promoted by regulatory, technological and commercial elements. Privacy regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) are applicable on a global scale and require organizations to handle sensitive data with care. This makes HE a very attractive option for computations on encrypted data. The growing sophistication and frequency of data breaches, cyberattacks and insider threats are a growing concern for data exposure.
This has led organizations to adopt measures to protect sensitive data even in untrusted environments. The HE permits organizations to outsource data processing or analytics without exposing raw data. This is crucial for the healthcare, government and finance industries. Homomorphic encryption makes it possible to train and pose queries to models on encrypted datasets. This has led to an increase in the use of machine learning (ML) and AI. The open-source libraries, more efficient algorithms, and improved encryption schemes are the results of continuous research and development. This has reduced the obstacles related to HE integration in modern computing systems.
Online shopping platforms often provide highly personalized recommendations based on user behavior, which can enhance customer experience. However, if these platforms misuse private information such as search history or purchase records, it can undermine consumer trust. Homomorphic encryption offers a solution by enabling algorithms to operate directly on encrypted data, allowing companies to generate accurate recommendations without accessing raw user information. This approach ensures that sensitive data remains secure while still delivering personalized shopping experiences. For businesses, this represents an opportunity to maintain customer satisfaction, protect privacy and minimize the risk of reputational damage due to data breaches.
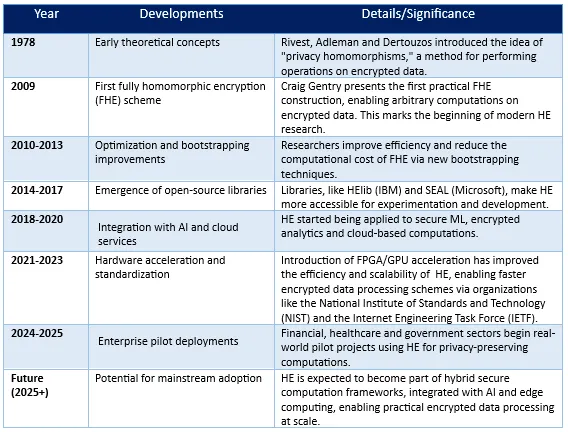
Evolution Timeline for Homomorphic Encryption
Factors Slowing Down the Adoption
Many businesses do not have the necessary expertise in crypto, parameter setting, algorithm optimization and hardware, especially if that expertise is integrated in an efficient and secure manner. Granted its promise, homomorphic encryption challenges stagnate its ultimate adoption, especially due to high computational costs. Tasks like encryption, operations on ciphertext, bootstrapping in fully homomorphic encryption, and decryption have significantly high latency, heavy CPU and memory usage and energy consumption fueled by computationally extensive operations.
Moreover, the lack of practical approaches to practical concerns means that the problem will only become more severe. With the growth of the data set, or an ever-growing query volume, memory and processing for a certain application will become exponentially impractical. The absence of law in benchmark and standard recognition leads industries to the decision that adopting it comes with a greater risk. Finally, the deployment of the high-performance computing infrastructure, storage, and withheld networking is unbearable to smaller organizations and real-time applications.
Future Outlook
Homomorphic encryption is advancing rapidly, with the potential to revolutionize entire industries. Companies now possess enormous amounts of sensitive information, and HE provides a means of analyzing and applying AI models to this data in its encrypted form. This allows no unauthorized entity to access the original data but still produces meaningful outcomes and advances that seem almost revolutionary. In addition to single organizations, HE facilitates safe multi-party cooperation. Several parties can conduct combined analytics without ever sharing raw data, resolving age-old privacy issues. These features could open the door to new services and innovative business partnerships that were once limited by confidentiality walls.
The regulatory climate also facilitates the adoption of HE. Globally, more stringent data privacy regulations ensure that secure computation becomes an appealing option, whereas improvements in hardware, algorithms and easy-to-use cryptographic libraries have made HE more viable and efficient than ever. With developers and businesses still exploring and optimizing HE, its integration into actual systems becomes increasingly smooth. Ultimately, with the proper technological environment and skills, homomorphic encryption will find a balance of security, usability and regulatory compliance, making it not just a technical enhancement but a subtle revolution for data privacy.
Where Things Stand and What's Next:
Transforming Healthcare Data Privacy and Analytics
Homomorphic encryption has grown from a specialized cryptographic idea to a revolutionary technology with broad implications across industries dealing with sensitive information, most notably, healthcare. It enables computation over ciphertext without decryption, thus maintaining data confidentiality during processing.
It is already being applied in areas such as medical diagnostics, heart rate monitoring, cancer research and secure analysis of health databases. In contexts where data privacy is paramount, HE is increasingly recognized as a practical and effective solution rather than a purely theoretical concept. Once regarded as a highly specialized and theoretical concept, HE is increasingly gaining practical traction. Recent regulatory requirements around data privacy are compelling organizations to adopt more rigorous measures for handling sensitive information, minimizing the risk of data breaches. With the growing adoption of AI and ML, particularly in sectors such as healthcare and banking, there is a heightened demand for performing sophisticated data analysis without directly accessing unencrypted data. This encryption enables precisely this, allowing computations on encrypted data while preserving confidentiality.
Cloud service providers and emerging "HE-as-a-Service" platforms are making the technology more accessible and cost-effective, reducing the barriers to adoption for organizations without extensive in-house expertise or specialized resources. Concurrently, advances in algorithms, hardware acceleration and open-source initiatives are improving the efficiency of homomorphic encryption, addressing previous performance limitations and enhancing its feasibility for real-world applications.
Looking for Consulting & Advisory Projects
