How FDA-Approved AI Tools are Revolutionizing Imaging Practices Across the Globe: Radiology’s New Ally
Challenges and Safety Considerations of AI-Driven Imaging

Each second countswhile detecting a tumor, diagnosing a stroke, or catching a hidden bleed. Nonetheless,radiologists worldwide are under pressure to process millions of scans morequickly and accurately. Long wait times, fatigue and delayed care have becomecommonplace issues that could have disastrous consequences when time is of theessence.
FDA-approvedartificial intelligence (AI) is the latest sort of partner that has entered thefray to combat the challenges. These clinically validated methods are no longerjust used in research labs; they are now being integrated into routineprocesses. AI supports radiologists in their quest to quickly, accurately andequitably deliver results that address the most urgent issues by identifyingthe critical ones, concentrating on them and simultaneously attending to bothemergency and community hospitals. It has been a long-standing belief thatradiology is the only field of modern medicine that is exclusivelytechnology-driven. However, the world now recognizes radiologists as one of thekey contributors to this process.
Why Radiology Needed an Ally?
Radiology is a medicalfield that produces the most images. A CT scan can generate numerous pictures,and a radiologist typically reviews hundreds of these studies each year. Withincreasing patient numbers and growing pressure for speed, radiologists oftenfeel exhausted and are at risk of missed diagnoses. Global shortages ofradiologists add to the existing pressure. For example, in some areas, there isfewer than one radiologist per 100,000 people. That is where AI comes in, notas a replacement for radiologists, but to support their skills and providequick, accurate care for each patient.
These challenges cancause delays, which can directly impact the survival of a patient in criticalsituations such as a stroke or trauma. Additionally, the intricate technologyrequired for modern imaging, such as multi-phase CT, high-resolution MRI andPET scan, further presents challenges that may be beyond the capabilities ofeven the most accomplished specialists. Therefore, radiologists need AI ratherthan it replacing them. When triaging patients, AI can make quicker decisions,detect subtle abnormalities and ensure that critical cases are prioritized.
FDA Approval: The Trust Seal
According to the U.S.Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the AI device's 700 algorithms have been approved, primarily for radiologic tasks, representing more than three-fourthsof the total. By obtaining FDA authorization, the algorithm demonstrated its utility and safety in specific clinical settings. It certifies to hospitals and doctors that these tools are not experimental—they are proven and ready forreal-world use.
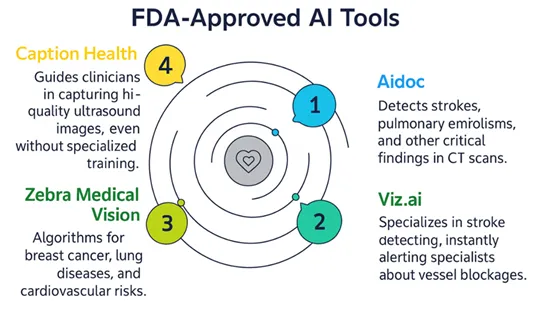
FDA clearance provides radiology AI a degree of legitimacy that accelerates real-world implementation.Compared with experimental software, FDA-approved algorithms have been stronglyvalidated for precision, safety and adoption in clinical routines. For instance,
- Aidoc (Israeli Aidoc Medical Ltd.) is a health technology company that offers AI-based solutions. These solutions are implemented in hundreds of hospitals worldwide to detect pulmonary embolism, stroke and cerebral hemorrhage early, reducing the risk of death from treatment delays.
- Zebra Medical Vision, an Israel based firm acquired by Nanox in 2021, developed FDA-approved algorithms for the detection of lung disease, cardiovascular diseases and cancers, that were aimed at population health screening.
- Caption Health (U.S., acquired by GE HealthCare in 2023) is known for Caption Guidance. This FDA-approved, AI-based ultrasound system enables doctors with limited training to obtain diagnostic-quality images.
- Viz.ai (San Francisco, USA), a leader in intelligent care coordination, implements AI-powered stroke triage tools that enable neurologists and radiologists to communicate instantly.
Each approval builds confidence in clinicians and serves as a globalreference point, making AI an increasingly trustworthy partner in healthcarediagnostics. Strategic partnerships that exemplify AI innovation aredemonstrated through FDA-approved tools in radiology. Aidoc and NVI used theBRIDGE framework to develop guidelines for public managers on the ethical andefficient adoption of trustworthy AI in real-world medical applications, bothlocally and globally.
GE HealthCare and Caption Health have collaborated to develop AIultrasound technology as a pilot for real NGO missions. Ultimately, whathappens at the end of such projects is like what we all strive for: being atthe forefront of invention, guided carefully to build legitimate trust andpromote the full, worldwide use of clinical AI.
Source: BCC Research
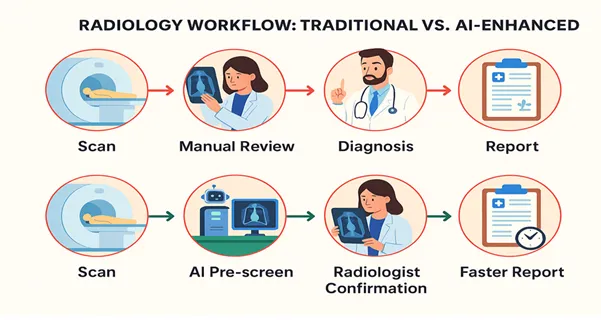
FromScan to Report: AI’s New Workflow
Earlier, the scanswould be fed into the system, remain in a long queue for human review andeventually be processed with a report. First, AI can perform initial screeningsof such images, detect deviations and sort the most relevant ones. Whileradiologists still make the final decision, with AI serving as their co-pilot,they can respond faster and with greater confidence. This workflow shift hastangible outcomes. In stroke treatment, where "time is brain," AI reduceddoor-to-treatment intervals by as much as 30 minutes, resulting in enhancedsurvival rates and patient outcomes. In breast cancer screening, AI-aidedinterpretations lowered false negatives by almost 9% and decreased recallrates. These benefits not only enhance patients’ lives but also save hospitalsmillions by reducing errors and legal risks.
Source: BCC Research
GlobalImpact Backed by Real-World Studies
The impact ofFDA-approved AI technology in radiology is no longer limited to the U.S. Itsspillover effects can be seen worldwide as other countries adopt similartechnology and modify their regulatory schemes. In Europe, CE-marked AI systemsare being increasingly adopted into national screening programs, particularlyfor the detection of breast cancer and monitoring lung diseases. Japan andSouth Korea, with their highly developed healthcare systems, have adopted AIimaging technology to deal with aging populations and radiology specialistshortages.
Several real-worldtrials demonstrate the quantifiable benefits of incorporating AI into thesystem. For instance, a multi-center study in the U.K. identified thatAI-assisted mammography had the potential to cut radiologists' workload byalmost half without sacrificing diagnostic quality. Another trial conducted inCanada demonstrated the benefits of faster triage of suspected strokes when CTscans were pre-screened by AI, resulting in up to 30 minutes of saved treatmenttime. Tuberculosis screening programs incorporating AI have yielded improvedearly detection rates in India, particularly in rural communities wherespecialist presence is limited.
FutureOutlook: Radiology of the Future
Radiology is enteringan era in which AI will go beyond detection to prediction and personalization.Emerging generative tools are already writing reports in real time, significantlyreducing reporting time, while multimodal foundation models are being trainedto read CT, MRI and radiographs at nearly radiologist-level proficiency. Thesetechnologies will not only identify disease but also track its progression andsupport more targeted treatment decisions.
Aidoc's recentintroduction of the BRIDGE framework, created in partnership with Nvidia, is anillustration of this change. The framework sets new benchmarks for the safescaling of clinical AI in the healthcare industry. The framework, which aims tofacilitate the use of AI in hospitals worldwide, achieves this by emphasizingstrong interoperability and transparent management as key elements in ensuringthe safe and efficient deployment of AI in hospital settings. Shibuya's ideasand breakthroughs illustrate how the coming era of radiology will encompass notjust performance improvement, but also trust, safety, and scalability. Theseadvances indicate how radiologists of the future will become orchestrators ofdiagnostic intelligence, combining the precision of AI with human empathy andjudgment to provide quicker, more patient-centric care worldwide.
Radiology tech AI isgetting better. It goes beyond simply finding things. Now, CT, MRI, PET andX-ray scans can all be viewed together quickly. Aidoc and NVIDIA's BRIDGE,Siemens and Microsoft Azure, and GE HealthCare are utilizing Caption Health'sAI ultrasound technology to help develop this new type of intelligent system.It mixes people's skills with the machine's accuracy. It's growing to be safeand good to use.
Conclusion
Radiology's path has alwaysbeen about clarity. With FDA-cleared AI solutions, that clarity is brighter,smarter, and quicker than ever before. AI is not replacing radiologists but isradiology's new partner, assisting in saving lives, streamlining workloads, andbringing care to more parts of the world. Notably, this union of radiologistsand AI represents a significant shift in the practice of medicine itself. Robustpartnerships and well-thought-out strategic investments have been the primaryfactors in advancing the industry to the next level. Medtech multinationalcompanies are seeking collaboration with AI startups and universitylaboratories to create closed-loop systems—devices that can automatically andinstantly stimulate nerves. These kinds of therapies, to be honest, are beingrolled out slowly by public and private healthcare organizations in the U.S.and Europe as part of their chronic disease management systems.
The future ofradiology is not about conflict between technology and humans, but rather aboutcollaboration between these two forces to improve the world.
Looking for Consulting & Advisory Projects
