The 10-Minute Charging Revolution: Niobium-Enhanced Fast-Charging Battery
The Rise of Niobium Batteries: A New Era in Energy Innovation
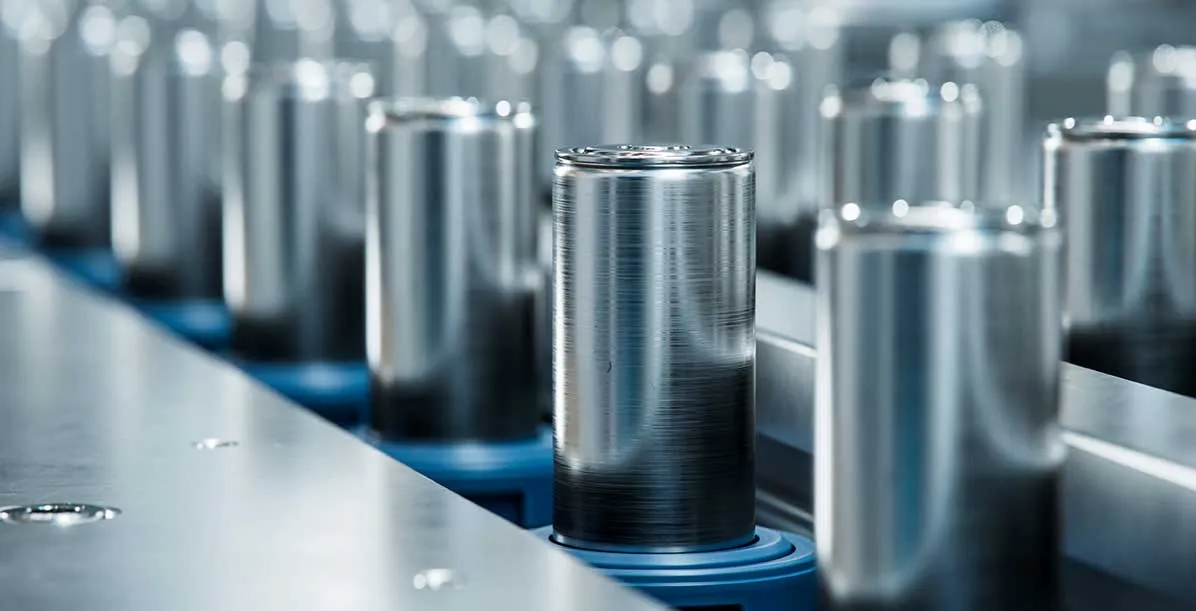

Benefits of Niobium
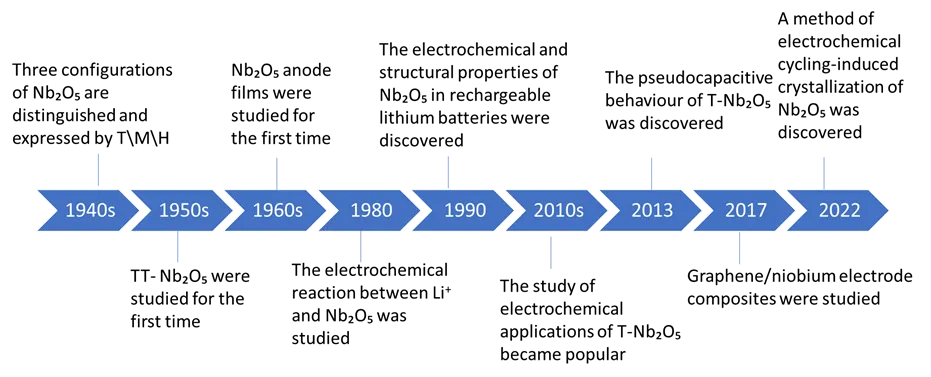
Evolution
The focus in battery technology research has shifted from simply using crystalline materials based on past studies to justified engineering of niobium oxide compounds, such as niobium-titanium oxide (Nb₂O₅) and niobium-tungsten oxide (NWO). The electrochemical performance of these engineered niobium oxide compounds exhibits significant rate capabilities and cycle lives, much higher than previously explored materials based on graphite or silicon. The figure below represents the historical research progress of Nb₂O₅.
Market Transformation: How Industry Adoption Is Scaling Niobium Battery Technology
- In June 2025, Toshiba, a major Japanese electronics company, made its debut with SCiB Nb batteries that use niobium titanium oxide anodes. Their technology works efficiently from -30°C to +60°C and can charge 80% of its capacity in 10 minutes, boasting a 15,000-cycle life.
- In April 2025, Nyobolt (the U.K.), a fast-charging battery technology company, raised $30 million to expand its business into new markets such as autonomous warehouse robots and heavy-duty vehicles, including mainstream electric vehicles.
- In June 2024, Echion Technologies (the U.K.) secured $35 million in Series B funding led by Volta Energy Technologies to implement its go-to-market strategy for its proprietary XNO (mixed niobium oxide) anode material. The innovation enables lithium-ion batteries to charge safely in under 10 minutes and retain more than 10,000 cycle life, solving the two main barriers to EV adoption.
- In November 2024, Echion and CBMM opened a niobium-based anode material production facility in Brazil. This facility is the first to manufacture niobium battery materials on an industrial scale, with an annual capacity of 2,000 tons, enough to produce 1 gigawatt-hour (GWh) of batteries.
- In September 2024, Leclanché launched XN50, the first Li-ion cell with XNO technology. It has a 50% higher energy density, fast charging and a cycle life of over 10,000 when used in heavy-duty applications.
- In line with its goal of reaching 40,000t of niobium oxide capacity by 2030, Companhia Brasileira de Metalurgia e Mineração (CBMM) invested $80 million in December 2022 to boost niobium oxide capacity from the current 500t to 3,000t.
Leading Companies and Their
Commercial Products
|
Company |
Technology |
Key
Performance |
|
CBMM (Brazil) |
NBXCELER
niobium oxide technology |
·
Provides better material efficiency. ·
Uses fewer raw materials, leading to
applications with a lower carbon footprint. |
|
Echion Technologies (U.K.) |
Niobium-based
XNO technology |
·
Achieves 80% state of charge in 3 to 10 minutes
of charging, ·
Exceeds 10,000 cycles with >12,000
cycles demonstrated. ·
Achieves up
to 425 Wh/L. |
|
Toshiba (Japan) |
Next-generation
SCiB using Niobium Titanium Oxide (NTO): SCiBNb |
The NTO
anode offers ultra-high-speed charging up to 90% of nominal capacity in 6
minutes, while maintaining 90% of its initial capacity after 5,000 charge-discharge
cycles. |
|
Nyobolt (U.K.) |
Niobium
tungsten oxide (NOW): a next-generation Li-ion battery technology |
·
Extremely
fast charging in <5 minutes. ·
15,000 to
20,000 full SoC (state of charge) charge-discharge cycles ·
Charge and
discharge from -200C to -600C
|
Future Outlook
Niobium-derived oxides (especially engineered forms of niobium pentoxide and niobium–tungsten oxides family) are expected to be the leading materials for ultra-fast-charging lithium-ion systems. Their dominant charge storage mechanism is pseudocapacitive or very fast intercalation, which eliminates Li⁺ diffusion limitations and enables stable operation at multi-C rates.
Over the next few years, these materials R&D will continue to bridge the gap between power and usable capacity through a series of phase/defect engineering, targeted doping (for example, tungsten and other cations), high-entropy strategies and conductive carbon architectures. In June 2025, Toshiba Corporation begins shipping its SCiB Nb lithium-ion battery innovation, enabling end users to recognize the importance of the electrification of buses, trucks and EVs. Niobium-based anodes are no longer a speculative laboratory curiosity; they possess a rapidly maturing materials platform for ultra-fast charging with established mechanisms, thus increasing industrial capability and clear engineering pathways to address current limitations.
Conclusion: The Ultra-Fast Charging Era Begins
Niobium-based batteries are becoming a viable option for achieving true ultra-fast charging in lithium-ion systems. Their underlying pseudocapacitive mechanism facilitates fast cycling, which minimizes structural damage. The ongoing improvement of doping, compositing and control of microstructure will continue to produce improvements in capacity and efficiency. Unlike many experimental anode concepts, niobium oxides are already moving into pilot-scale production and are being demonstrated in vehicles. In June 2024, Nyobolt (the U.K.) moved its high-power density, fast-charging battery technology from the lab to the real world with the announcement of its first running Nyobolt EV sports car prototype. There is sufficient research and industry activity to suggest that niobium-based fast charging technology will continue to develop, striking a balance between current limitations with the evident strengths of power and durability.
Looking for Consulting & Advisory Projects
