Robotic Process Automation in Medical Billing and Administration
Clear insight into competitor positioning and market share.

Robotic Process Automation in Medical Billing and Administration: A Practical Roadmap
A significant shift is emerging in the fundamentals of healthcare administration that helps with medical billing and other routine tasks. Robotic process automation (RPA) id recognized as an increasingly used technology with a profound impact on the way hospitals, physician groups and revenue cycle management (RCM) companies collaborate.
According to the Medical Group Management Association (MGMA), hospitals that automate their billing workflow report a reduction in denials by up to 50%. Automated claim scrubbing can result in a first-pass resolution rate of over 95%. Practices that have implemented an automated system for charge capture and real-time claim tracking have reduced their days in accounts receivable to 40 or fewer and achieved net collection rates above 96%, which are milestones that manual systems cannot sustain.
What’s Driving the Rush to RPA?
The medical billing and administration sector is characterized by repetitive, rule-based workflows and a high volume of tasks, such as claims submission, eligibility checks, denial handling, payment posting, auditing and more. These are precisely the kinds of processes that are suitable for RPA.
The Healthcare Business Management Association’s (HBMA’s) RCM Advisor has been a source of stories about the healthcare industry's billing revenue cycle, spanning from completely manual to digital automation, within the healthcare billing domain. At the same time, hospitals and researchers are forecasting that the combination of RPA with cognitive capabilities, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and natural language processing (NLP), will enable automation to semi-structured inputs; the impact varies by workflow. The American Hospital Association mentions that roughly 46% of hospitals have already adopted AI in their revenue-cycle operations, and 74% are using some form of automation in the revenue cycle (which includes RPA).
Key Advantages Driving RPA Adoption

Adopting RPA in medical billing aims to enhance the accuracy, scalability, and robustness of the revenue cycle, while also modernizing processes. Organizations are experiencing quantifiable improvements in speed, accuracy and financial performance, ranging from big hospital networks to mid-sized medical practices. For instance, Massachusetts Health utilized RPA to enhance accuracy and compliance rates while streamlining its Medicaid claims process and accelerating reimbursements without the need for additional staff.
Key Workflow Transformation Areas
To stimulate action, here are the high-impact use cases where RPA (and intelligent automation) is already redefining operations:
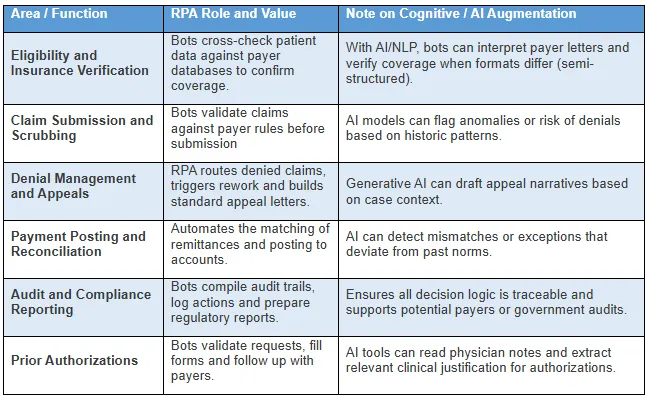
Note - Table is Illustrative and would vary by payer
mix and integration depth
These are not academically “future use cases”; many billing/RCM firms have already launched or are in the process of piloting such automations. According to Medwave, RPA is already changing the scenario of manual entry in medical billing by fetching data from multiple sources and auto-filling billing forms, thus lowering the chance of transcription errors and reducing the need for human intervention. AnnexMed highlights the effects of quicker claims processing, fewer denials, increased data accuracy and more staff time for exception handling and revenue recovery.
The Automation Advantage: Why Acting Now Matters?
1. Denials and Rejections Are Punishing Margins
Intelligent payers using AI are imposing stricter regulations and increasing the number of denials. Robotic process automation can be utilized for pre-validation of claims and to automate the appeal process, thereby averting revenue loss and safeguarding cash flow.
2. Labor Costs and Staffing Shortages
One should not underestimate administrative burnout. Automation using technology can increase the scale of operations without the need to physically expand the team, allowing organizations to effectively handle the rising volume of claims.
3. Regulatory and Audit Compliance
Robots keep precise records of the entire process and strictly adhere to the rules. Therefore, they help to comply with controls, generate exportable audit logs, facilitate reporting and reduce the risk of being checked.
4. Revenue Leakage and Delayed Payments
Inaccuracies in the manual coding or reconciliation process not only waste time but also cost money. RPA ensures the standardization of workflows and eliminates the concealment of revenue that, if left unchecked, can lead to a loss of margins.
5. Innovation Momentum Is Irreversible
The leaders of the industry are already on the way to implementing automation in their billing processes. There is not just an opportunity cost in catching up late, but you risk falling behind on throughput and accuracy metrics.
Strategic Outlook
The healthcare world needs more efficient and simplified administrative processes all the time. Models of value-based care are those that ultimately reward outcomes and efficiency, rather than manual effort. As payers continue to automate their processes, they will remain less tolerant of errors and delays from providers for some time to come. The price of RPA implementation is no longer the major issue it once was. The real challenge lies in the consequences of inaction, which include lost revenue, staff burnout, compliance risks and the operational advantage of competitors, which continues to grow.
The discussion is no longer about whether practice should use RPA, but rather how quickly it can be implemented to prevent setbacks. It is no longer a matter of anticipating future developments. The future is already there at the billing office down the street. Your future depends on catching up.
Looking for Consulting & Advisory Projects
