Ultra-Low Power Edge AI Chips for Medical IoT Devices: A Call to Build What’s Next
Energy-Efficient AI Chips Powering Smart Medical IoT Devices

The need for more intelligent and effective devices is greater than ever in the quickly changing field of medical technology, particularly in the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) space. Medical IoT devices can now run sophisticated AI algorithms locally without depleting battery life—thanks to ultra-low power edge AI processors, which are becoming an essential enabler of this capability. These customized chips process data in real time while using a fraction of the power of conventional processors, drawing inspiration from the human brain's energy-efficient architecture. For wearable health monitors, devices that are implanted, and remote sensors that require continuous operation for extended periods with minimal maintenance, this efficiency is crucial. These chips enable better data security and system flexibility, as they handle data on the spot, thereby reducing reliance on cloud connectivity. Ultra-low power edge AI chips are more than just a technical advancement as healthcare moves toward proactive, individualized care. They are a call to develop the next generation of smarter, safer and more dependable medical devices. To create the next wave of healthcare technology, developers, physicians and patients can all benefit from exploring this area.
Evolution
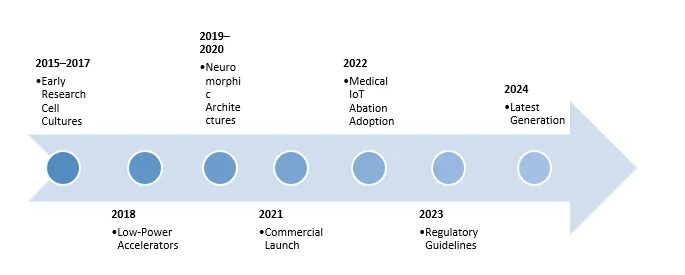
Ultra-low power edge AI chips for medical IoT
devices have advanced quickly and significantly. From 2015 to 2017, the first studies
concentrated on energy efficiency and fundamental biological applications. By
2018, wearable AI had become possible with the development of low-power
accelerators. Inspired by the efficiency of the brain, neuromorphic
architectures first appeared in 2019 or 2020, offering sophisticated
physiological monitoring capabilities. In 2021, ultra-low power AI chips specifically
designed for the Internet of Things (IoT) were commercially released, enabling
on-site, real-time data processing. As IoT medical devices gained popularity
for ongoing health monitoring, adoption increased dramatically in 2022.
Regulatory frameworks guaranteeing the safety and integration of AI chips in
clinical settings emerged in 2023. In 2024, chips have advanced to provide near
real-time processing, multi-modal sensing and improved security, opening the
door for medical IoT to provide more intelligent, effective and individualized
healthcare solutions.
Evolution of Ultra-Low Power Edge AI Chips for Medical IoT
What Are Ultra-Low Power Edge AI Chips?
At its core, edge AI refers to bringing AI directly onto the devices that collect data, rather than sending everything to the cloud for processing. Ultra-low power edge AI chips take this a step further. These are cleverly engineered to run on incredibly tiny amounts of energy, sometimes measured in microwatts or milliwatts, enabling devices to operate for years on small batteries or harvested ambient energy.
What makes them tick? Some incorporate brain-inspired architectures, such as neuromorphic or event-driven processing, which mimic how neurons fire only when something important happens, thereby avoiding wasted effort that occurs when running all the time. Others utilize cutting-edge circuit designs and optimized wireless modules that extract every drop of efficiency from the available power.
For example, chips built on Ambiq’s SPOT platform minimize energy use during idle periods, stretching battery life far beyond traditional limits. Meanwhile, BrainChip’s neuromorphic AI, paired with ultra-efficient wireless connectivity, enables sensors to operate on microwatts, making them ideal for always-on health monitoring.
Why They Matter in Medical IoT?
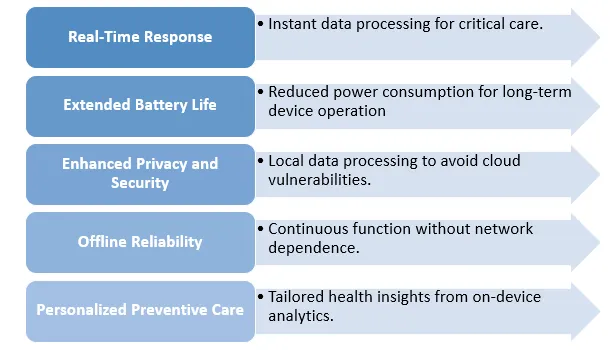
- There is no room for error or downtime since the healthcare sector is different from other sectors. Medical equipment frequently monitors vital signs, blood sugar, heart rhythms and brain activity continuously, sometimes for months or even years.
- Real-Time Response: Edge AI makes it possible to identify anomalies instantly and initiate notifications or actions at once. Waiting for data analysis from cloud servers can result in risky delays. This real-time processing, as noted by Voler Systems, can avert major health crises and provide decision support at the precise moment required.
- Extended Battery Life and Usability: Frequent recharging or battery replacement in a medical device is undesirable. Care is continuous rather than intermittent due to ultra-low power designs, which make devices smaller, more practical and more likely to be worn or implanted over time.
- Improved Security and Privacy: Patient information is highly sensitive. Local data processing minimizes hacking risks and helps organizations comply with strict laws, such as HIPAA or GDPR, thereby preserving trust among patients, providers and manufacturers.
- Reliable Even Offline: Many patients face network outages or live in areas with unreliable internet connections. In these cases, edge AI-powered devices can operate effectively, ensuring safety and monitoring.
- PPersonalized Preventive Care: In addition to handling emergencies, edge AI chips allow devices to identify early warning signs and adapt to each user's unique health routines, helping to prevent disease before it develops.
Key Benefits of Ultra-Low Power Edge AI Chips for Medical IoT Devices
Current Trends in Technology
- Below are the current trends in technology, accompanied by dated examples and primary sources. The field is accelerating rapidly with real-world advancements proving the concept.
- BrainChip and HaiLa’s 2025 collaboration merged neuromorphic AI with hyper-efficient wireless backscatter connectivity, creating sensors that run continuously on microwatts. This breakthrough could enable ongoing monitoring of cardiac irregularities or neurological conditions without the need to swap batteries.
- Ambiq’s Apollo System-on-Chip (SoC) series, built on their SPOT technology, is powering a new wave of health wearables that are designed for extended operation. Its actual runtime depends on the workload and duty cycle, making continuous health tracking seamless and practical.
- Neuromorphic chips that employ event-driven spiking models minimize idle computation to achieve sub-milliwatt inference in wearables and near-body patches. However, implantable use is still at the pilot stage and requires further validation.
- Integration of sensing, computing and wireless communication into cohesive, ultra-efficient platforms is increasingly common, reducing system-wide energy waste and maximizing device lifetime.
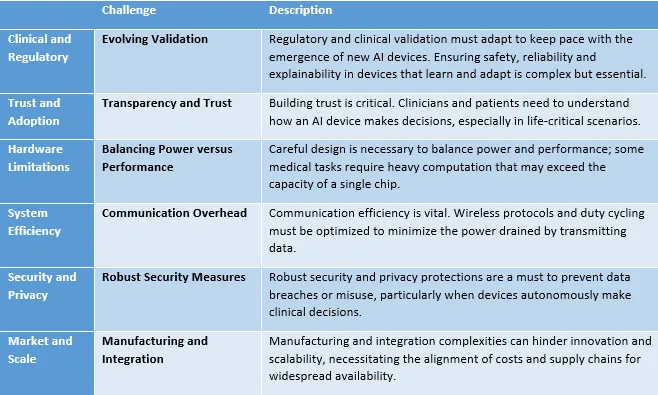
The Challenges We Still Face
Where Should Industry Stakeholders Focus Their Efforts Today?
- If your work intersects with medical devices, IoT, or AI chip technology, now is the time to:
- Thoroughly review power budgets for existing and upcoming devices, aiming to move more intelligence to the edge and trim unnecessary communication.
- Collaborate closely with chipmakers specializing in neuromorphic or ultra-low power designs to co-create systems that embrace on-chip learning and minimize standby power.
- To better understand performance, energy consumption and false alarm rates, prototypes should undergo thorough testing in real-world environments such as homes, clinics and various other locations.
- Invest in fail-safe procedures and explainable AI models to build trust with regulators, patients and clinicians.
- Engage regulatory agencies early to speed up certification processes and shape evolving standards.
- To further minimize energy drains, optimize infrastructure usage and communication methods.
- Pay attention to advanced scholarly and commercial research that may soon expand the realm of the possible.
Future Outlook
- To stay ahead, keep an eye on the following emerging trends and capabilities:
- AI chips capable of learning and adapting on the device itself, tailoring behavior to individuals and environments over time.
- Memory innovations that minimize power use during both inference and learning.
- New sensor types that only produce data when relevant changes occur, saving energy.
- Devices powered in part or wholly by harvested ambient energy, further extending lifetimes.
- Growing toolkits and frameworks that simplify developing and certifying edge AI medical devices.
Your Move
Ultra-low power edge AI chips are enabling the creation of a new generation of medical IoT devices—designed to be reliable, secure, intelligent and virtually maintenance-free—delivering the standard of care patients truly deserve. Now is the moment for regulators, semiconductor innovators, healthcare providers and medical device manufacturers to embrace transformative technologies. Begin incorporating these technologies, take calculated risks, collaborate widely and communicate openly with users and regulators. The future of healthcare will be shaped by the gadgets you help design today—always on, always aware, yet kind to both lives and resources.
The technology has arrived. The opportunity is yours. What will you build next?
Looking for Consulting & Advisory Projects
